
Are the Stars We See at Night Still There?
Have you ever looked up at the night sky and wondered if those glittering stars are still really there? It’s a question that blends curiosity with cosmic scale, and the answer lies in a mix of astronomy, physics, and a little poetic wonder.
Let’s explore the fascinating truth behind what we’re really seeing when we gaze at the stars.
Light doesn’t travel instantly. It moves at about 299,792 kilometers per second. That’s incredibly fast, but the universe is vast. Even the light from our closest star (besides the Sun), Proxima Centauri, takes over 4 years to reach us.
The bright stars you see at night? Many of them are hundreds or even thousands of light-years away. That means the light you’re seeing tonight left those stars centuries ago. In essence, you’re looking into the past, a natural time machine.
But here’s the big question: Are those stars still alive today, or have some of them already died out?
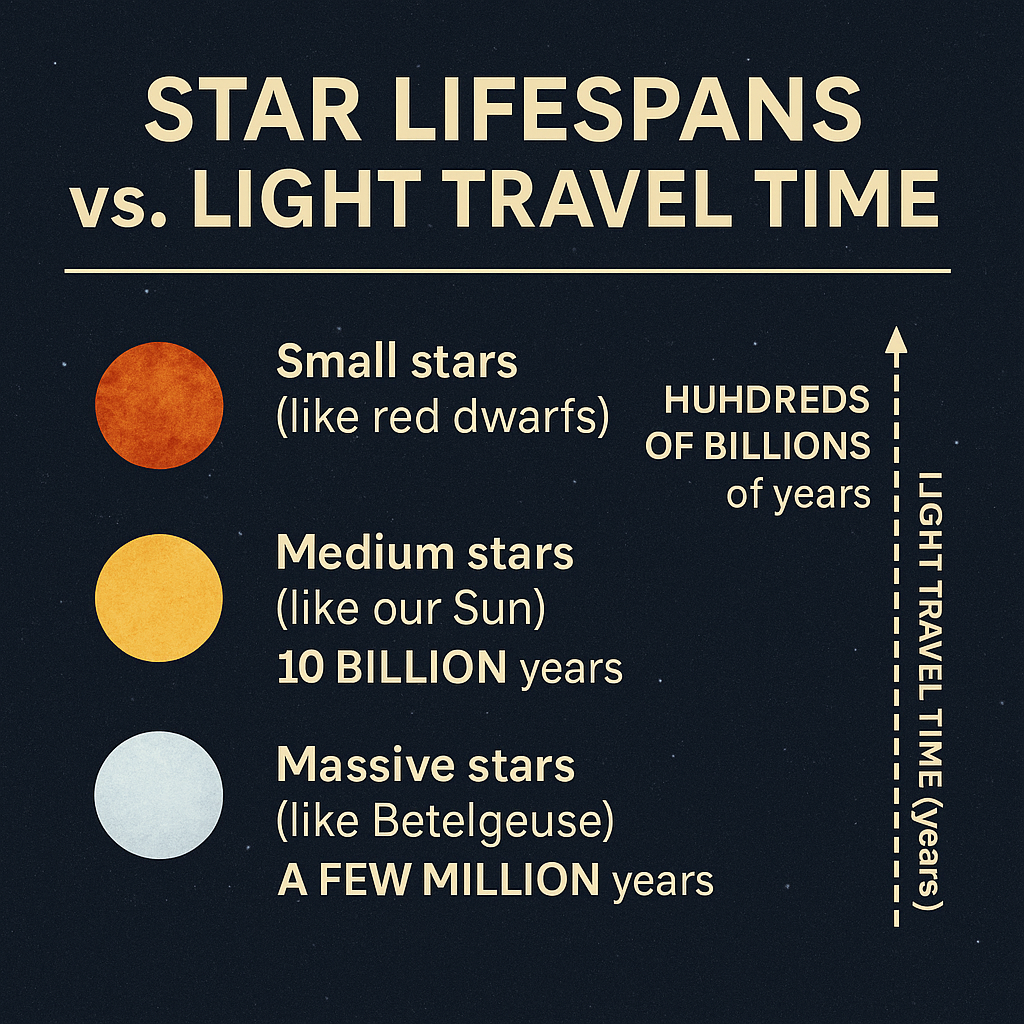
Stars, like everything in the universe, have a lifespan. Some live fast and die young, while others burn slowly and steadily for billions of years. A star’s life depends mostly on its size:
- Small stars (like red dwarfs): burn for hundreds of billions of years
- Medium stars (like our Sun): live for about 10 billion years
- Massive stars (like Betelgeuse): may last only a few million years
Now compare that to how long their light takes to reach us. Even a very distant bright star is typically only a few hundred to a thousand light-years away, meaning we’re seeing it as it was just a few centuries or millennia ago.
That’s a very short time compared to the millions or billions of years these stars live. So the answer becomes clear: Almost all the stars we see with our eyes are still alive.
Let’s Look at Some Famous Stars
Here are a few of the night sky’s most recognizable stars and where they stand:
🌟 Sirius
- Brightest star in the night sky
- Only 8.6 light-years away
- A young, stable star expected to live for over a billion years
✅ Still shining
🔴 Betelgeuse
- A red supergiant in Orion
- Around 500 light-years away
- Nearing the end of its life, expected to go supernova sometime in the next 100,000 years
✅ Still shining, but astronomers are keeping an eye on it
🔵 Rigel
- A blue supergiant also in Orion
- About 860 light-years away
- A few million years old, but still going strong
✅ Still shining
⭐ Polaris (The North Star)
- Around 440 light-years away
- A supergiant star with millions of years left in it
✅ Still shining
Could Any Have Died Already?
Technically, it’s possible. A very massive star could have gone supernova in the time its light has been traveling to us. But we’d almost certainly notice the explosion. Supernovae are bright, dramatic, and visible even during the day when they occur.
There’s no confirmed case of a naked-eye star simply vanishing in recent history.
So, Are We Staring at Ghosts?
Not quite. What we see is the past light of living stars. They’re not ghosts, but more like old postcards still arriving in the mail. The odds are overwhelmingly in favor that the stars you see tonight are still there.
It’s a comforting thought, isn’t it? Amid the chaos of life on Earth, those familiar stars have been shining, and will continue to shine, far longer than most things we know.
So next time you’re stargazing, take a moment to reflect. You’re witnessing ancient light from cosmic companions that are still burning bright across the universe.
Keep looking up. The universe is alive, and so are the stars you see.
Citations:
https://www.skyatnightmagazine.com/space-science/space-night-sky-look-back-in-timeHow Far Are Stars? | Do the Mathhttps://dothemath.ucsd.edu/2024/05/how-far-are-stars/Sirius – Wikipediahttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SiriusBetelgeuse – Wikipediahttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BetelgeuseMain Sequence Lifetime | COSMOShttps://astronomy.swin.edu.au/cosmos/m/main+sequence+lifetimeMain Sequence Stars: Definition & Life Cycle | Spacehttps://www.space.com/22437-main-sequence-star.htmlBetelgeuse – Wikipediahttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BetelgeuseBlue-white Rigel is Orion’s brightest starhttps://earthsky.org/brightest-stars/blue-white-rigel-is-orions-brightest-star/Rigel – Wikipediahttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RigelPolaris – Wikipediahttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PolarisPolaris – Wikipediahttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PolarisSirius – Wikipediahttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sirius